[Matplotlib.pyplot] 07. Histogram
Updated:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
1. hist
matplotlib에서 히스토그램을 그리기 위해서는 Axes.hist()를 사용해야한다.
Axes.hist(x,bins=None,density=False,cumulative=False,orientation=’vertical’,align=’mid’)
- x: histogram으로 표현할 값
- bins: 간격 수
- density: y축이 갯수가 아닌 probablity density를 표현한다. probability가 아닌 density임에 주의하자! (면적이 1)
- cumulative: 누적 갯수
- orientation: ‘vertical’, ‘horizontal’ 중 선택
- align: ‘left’, ‘mid’, ‘right’ 중 선택
- 그 외 parameter는 api 참고
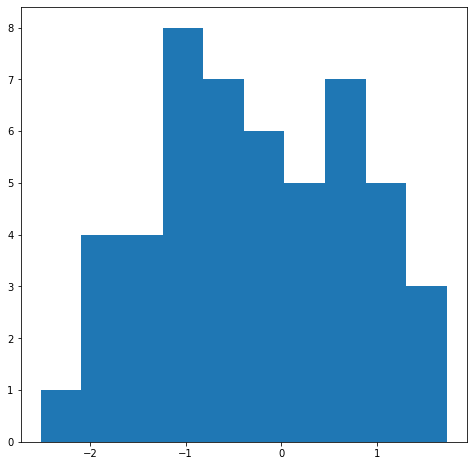
n_data = 50
fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8,8))
x = np.random.randn(n_data)
ax.hist(x)
(array([1., 4., 4., 8., 7., 6., 5., 7., 5., 3.]),
array([-2.51332481, -2.08928554, -1.66524627, -1.241207 , -0.81716773,
-0.39312846, 0.03091081, 0.45495008, 0.87898935, 1.30302862,
1.72706789]),
<BarContainer object of 10 artists>)

n_data = 50
fig,axes= plt.subplots(2,1,figsize=(8,8))
x = np.random.randn(n_data)
axes[0].hist(x)
axes[1].hist(x,bins=20)
(array([2., 0., 2., 2., 1., 1., 4., 9., 4., 5., 2., 4., 0., 5., 5., 0., 3.,
0., 0., 1.]),
array([-2.28411285, -2.05300787, -1.82190289, -1.59079791, -1.35969293,
-1.12858795, -0.89748298, -0.666378 , -0.43527302, -0.20416804,
0.02693694, 0.25804192, 0.48914689, 0.72025187, 0.95135685,
1.18246183, 1.41356681, 1.64467179, 1.87577676, 2.10688174,
2.33798672]),
<BarContainer object of 20 artists>)
n_data = 50
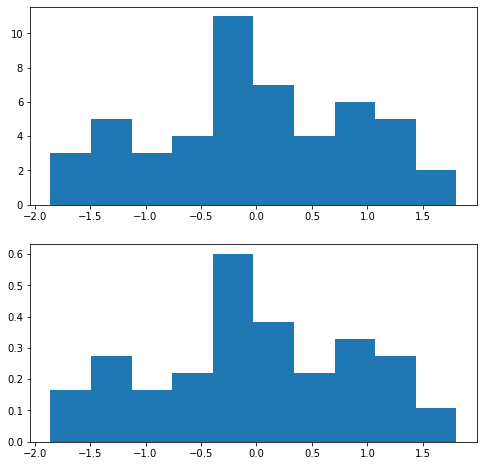
fig,axes= plt.subplots(2,1,figsize=(8,8))
x = np.random.randn(n_data)
axes[0].hist(x)
axes[1].hist(x,density=True)
(array([0.16399127, 0.27331878, 0.16399127, 0.21865503, 0.60130132,
0.3826463 , 0.21865503, 0.32798254, 0.27331878, 0.10932751]),
array([-1.85722033, -1.4913472 , -1.12547406, -0.75960093, -0.39372779,
-0.02785466, 0.33801848, 0.70389161, 1.06976475, 1.43563788,
1.80151102]),
<BarContainer object of 10 artists>)

n_data = 50
fig,axes= plt.subplots(2,1,figsize=(8,8))
x = np.random.randn(n_data)
axes[0].hist(x)
axes[1].hist(x,cumulative=True)
(array([ 4., 5., 10., 18., 25., 34., 39., 44., 49., 50.]),
array([-2.00284619, -1.62049593, -1.23814567, -0.8557954 , -0.47344514,
-0.09109488, 0.29125539, 0.67360565, 1.05595591, 1.43830618,
1.82065644]),
<BarContainer object of 10 artists>)
n_data = 50
fig,axes= plt.subplots(2,1,figsize=(8,8))
x = np.random.randn(n_data)
axes[0].hist(x)
axes[1].hist(x,orientation='horizontal')
(array([ 2., 1., 2., 3., 10., 10., 6., 9., 3., 4.]),
array([-2.57089357, -2.12521051, -1.67952746, -1.2338444 , -0.78816135,
-0.34247829, 0.10320476, 0.54888782, 0.99457087, 1.44025393,
1.88593699]),
<BarContainer object of 10 artists>)

2. n, bins, patches
Axes.hist()는 다음 3가지를 반환한다.
- n: The value of the histogram bins. 각 막대가 지닌 높이를 담은 array를 반환한다.
- bins: the edge of bins. 즉 Axes.hist() parameter의 bins가 총 10개라면 edge는 11개가 된다.
- patches: Rectangle Object를 담은 Bar Container를 반환한다.
- get_x(), get_width(), get_height()를 사용하여 활용 가능
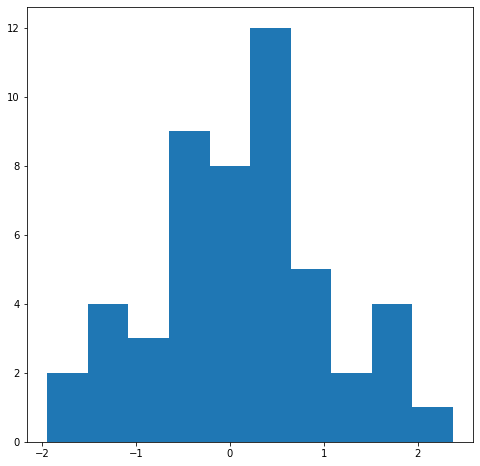
n_data = 50
x = np.random.randn(n_data)
fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8,8))
# 이름을 바꾸어서 표현
heights, bin_edges, rects = ax.hist(x)
print(heights)
print(bin_edges)
print(rects)
[ 2. 4. 3. 9. 8. 12. 5. 2. 4. 1.]
[-1.94514072 -1.513107 -1.08107328 -0.64903956 -0.21700583 0.21502789
0.64706161 1.07909533 1.51112906 1.94316278 2.3751965 ]
<BarContainer object of 10 artists>

n_data = 50
x = np.random.randn(n_data)
fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8,8))
# 이름을 바꾸어서 표현
heights, bin_edges, rects = ax.hist(x)
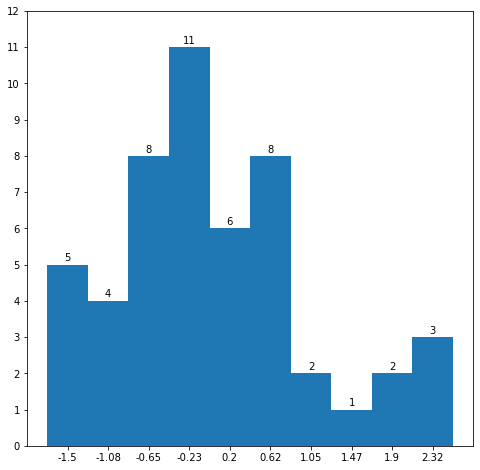
# lims
ymax = max(heights)
ax.set_ylim([0,ymax+1])
# tick
bin_center = (bin_edges[:-1] + bin_edges[1:]) / 2
ax.set_xticks(bin_center)
ax.set_xticklabels(bin_center.round(2))
yticks = np.arange(ymax+2,dtype=np.int8)
ax.set_yticks(yticks)
ax.set_yticklabels(yticks)
for idx in range(len(heights)):
ax.text(bin_center[idx],heights[idx]+0.1,int(heights[idx]),ha='center')
Leave a comment